
ESG (Environmental Social Governance) is an approach to conducting business that incorporates several non-financial metrics in three key areas: environmental, social, and governance. With demand for transparent and sustainable business practices at an all-time high, companies must have an ESG strategy in place to meet investor, customer, employee and regulator expectations.
In this ESG program guide, we break down the basics of ESG as well as its importance. We'll provide guidelines and examples of ESG strategic roadmaps along with steps to formally start your own ESG program.
Table of Contents
ESG is a holistic approach to business that goes beyond maximizing shareholder profits to address environmental, social, and corporate governance impact for all stakeholders.
Through ESG, businesses define and measure their impact on the environment and society while remaining transparent about their governing practices. The goal is to ensure businesses remain intentional about fostering sustainable and ethical operations for people and the planet.
ESG is important for companies, employees, investors, and consumers.
✔ ESG is important for companies because investors, customers, community members and regulators are demanding it. Investors are increasingly attuned to the long-term risk to growth posed by companies that overlook issues such as climate change. Customers are looking for companies to purchase from that prioritize ethical and sustainable practices. Community members seek assurance that companies are taking local sustainable development concerns into account. Under pressure from all three other stakeholder groups, regulators are putting requirements in place for business to report on metrics that are consistent, comparable and reliable.
✔ ESG is important for employees because they wish to work for companies that share their values and place importance on ESG principles. Employees want to be a part of companies dedicated to serving a greater purpose. This leads to fulfillment within their careers, something all employees wish to experience.
✔ ESG is important for investors because companies that overlook ESG-specific issues such as social inequality and climate-related impacts pose a greater long-term risk. In contrast, companies focused on ESG are better positioned for long-term growth.
The benefits of ESG go even further. For example, companies that invest their time and effort into ESG may experience:
The terms ESG and CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) are often used interchangeably. Some believe CSR was the first form of ESG. While both ESG and CSR help companies conduct ethical and sustainable business practices, the approach is different.
CSR refers to the methods companies use to prioritize environmental and social concerns. In contrast, ESG clearly defines those methods and measures the impact of environmental, social and governance efforts within the company and on the communities in which it operates. ESG includes specific criteria businesses must meet.
Through CSR, a business may aim to hire a more diverse workforce. For businesses with an ESG strategy, however, that goal becomes a measurable metric in a set timeframe. For example, the ESG company might seek to hire 10% more women by the end of the fiscal year.
ESG and sustainability focus broadly on the economy, people and the environment. ESG includes measurable and specific indicators that address all aspects of the environment, society and business governance.
Sustainability is sometimes confused with a narrow environmental nexus; however, it refers to a company’s holistic efforts to balance people, planet and profit. Sustainability was defined by the United Nations (UN) Brundtland Report, published in 1987, as “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” This approach is the basis of the UN Global Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) – one of the broadly accepted ESG frameworks used to align business strategy with solutions to key environmental and social issues.
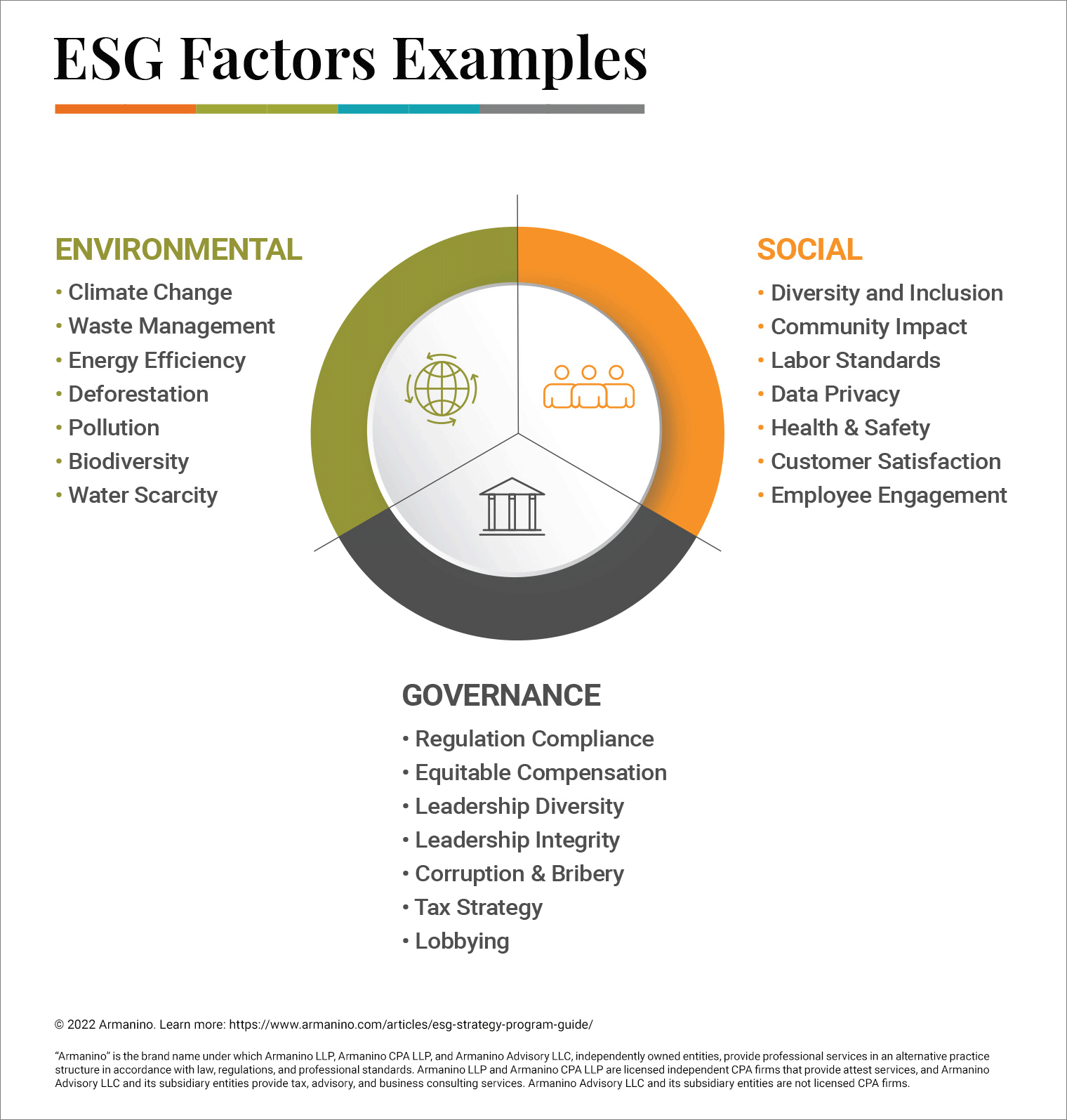
ESG is composed of three factors -- Environmental, Social, and Governance. (Note: Beware of differing semantics -- the term “factors” is often used interchangeably with “criteria,” “issues” and “risks” amongst different ESG frameworks, rating agencies, or references.)
The ESG environmental factors focus on how a company impacts natural resources and manages environmental risks.
The ESG social factors focus on stakeholder relationships -- including relationships with employees, customers and society as a whole.
The ESG governance factors focus on how a business is governed, including how decisions are made, who makes decisions regarding the business and how processes are completed.
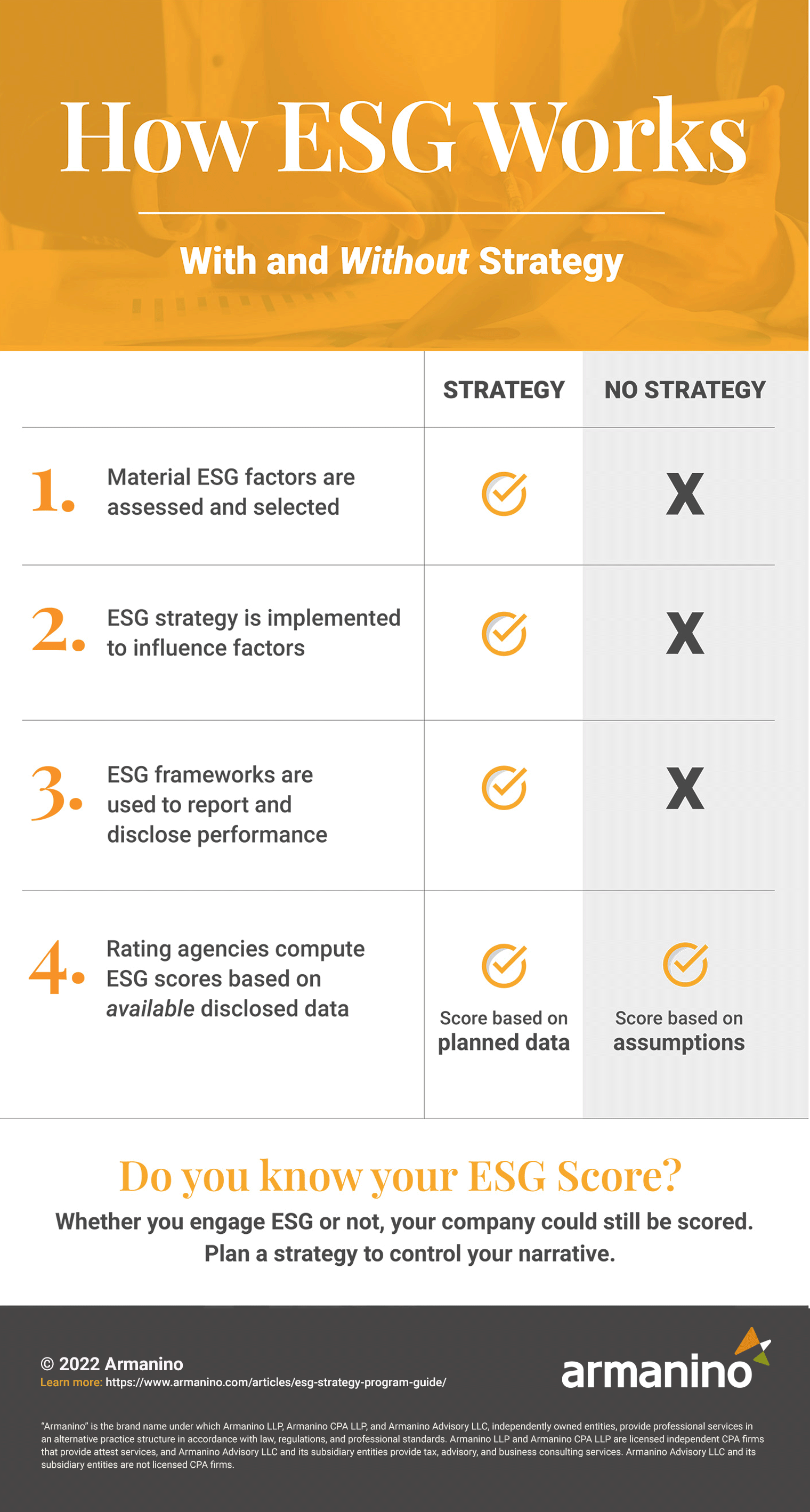
Perhaps the most critical thing to understand about ESG is that regardless of whether you have a formal ESG program strategy, your company likely has an ESG score.
The critical difference with having a strategy is that you can guide your company’s ESG narrative with prioritized goals, strategic planning and transparent results, instead of some analyst making assumptions.
Want to display this infographic on your site? Copy and paste the following code. Be sure to include attribution to armanino.com with this graphic.
An ESG strategy is an action plan to achieve environmental, social, and governance goals that align with a company’s vision, values and growth plan. It’s the roadmap companies follow to ensure they’re doing what they say they’re going to do – capturing opportunities, avoiding risks and meeting all necessary regulatory requirements.
A strategy typically outlines the why (mission), what (goals/metrics), how (tactics) and when (timeframe) for an initiative. A strategic roadmap ideally includes all those components; however, many companies only publish goals and target dates for external audiences.
Your ESG strategy should answer:
Note: A strategy differs from an action plan in that it evaluates multiple options for execution and then selects tactics that will best facilitate goal completion. Background work that goes into tactic selection isn’t always apparent, so some strategies look just like an action plan. Make sure you evaluate more than one tactical approach for ESG, so your plan is truly “strategic.”
There are many different approaches to ESG, so an organized, strategic approach is vital for success.
A strong ESG strategy:
Strategic roadmaps come in all shapes in sizes. We’ve provided multiple examples below to help inspire what info to include and how to best present it.



An ESG program refers to the policies, measures, and activities that a business has in place to manage environmental, social and governance factors pertinent to stakeholders and business success.
To take advantage of the many benefits of ESG while doing their part to realize a more equitable society and sustainable environment, businesses should develop formal ESG programs. High-level steps have been provided below:

Want to display this infographic on your site? Copy and paste the following code. Be sure to include attribution to armanino.com with this graphic.
Jumpstarting an effective ESG program can be a daunting process. Do you know which ESG factors have a material impact for your business? Which ESG framework is best for you? Reach out to our ESG consultants today for an ESG assessment and strategic roadmap.
From risk assessments and framework selection to report guidance and independent assurance of data, our team can assist your ESG strategy and efforts.