
ESG (Environmental Social Governance) scores or ratings measure a company’s ESG efforts. These scores help communicate a company’s sustainable business practices to both stakeholders and investors. They also assist companies in understanding their ESG shortcomings and how they might improve their ESG strategy or ESG reporting.
In this guide we’ll discuss the importance of ESG scores, known challenges with score standardization, how to find your score, and how to improve your score. We additionally detail the 9 most popular ESG rating agencies to help compare and contrast their value and relevance for your company.
Table of Contents
An ESG score or rating is the measure of a company’s environmental, social, or governance perceived risk or overall performance. These scores are used by investors who want to understand a company’s long-term risk as well as by consumers who wish to make more informed purchasing decisions.
Most of the time, an ESG score or rating is given based on how a company performs when compared to its peers. These scores take into account everything from how a company manages environmental risks to how well it emphasizes workplace diversity.
Of course, score and rating criteria will differ depending on the rating agency delivering the score.
ESG “score” and ESG “rating” are used often interchangeably. A key difference lies in the use of numerical scores and letter ratings, which differs between rating agencies.
For example, MSCI uses letter ratings ranging from CCC (Laggard) to AAA (Leader). ISS uses numerical scores ranging from 1 (best) to 10 (worst). Other organizations such as S&P Global publish sustainability ratings in classes, like “S&P Global Silver Class.”
Regardless of whether an agency uses a score or a rating, the goal of the result is still the same: to show a company’s ESG performance in a tangible, comparable way.
A “good” ESG score will differ depending on the rating system. High scores aren’t necessarily best. For example, using DJSI, Refinitiv, or Bloomberg a score of 0 is poor. However, using Sustainalytics, a score of 0 is best (negligible risk.)
For companies who wish to achieve a good ESG score, the goal should be to meet ESG best practices. Companies can do so in many ways. For example, they can perform materiality assessments to determine ESG goals, follow ESG frameworks, and publish relevant ESG disclosure reports to communicate their efforts.
ESG ratings are important to communicate ESG goals and progress with stakeholders and potential investors. For example, ESG ratings:
Although ESG scores are useful tools for stakeholders, they can be problematic as various challenges exist.
Do you know your company’s ESG score? Even if you didn’t disclose an ESG report, you still might have a public score.
To find a company’s ESG score, first try Googling the company’s name plus “ESG score”. (Google query example: microsoft esg score) For specific scores, visit the rating agency website directly. Some popular score lookups include:
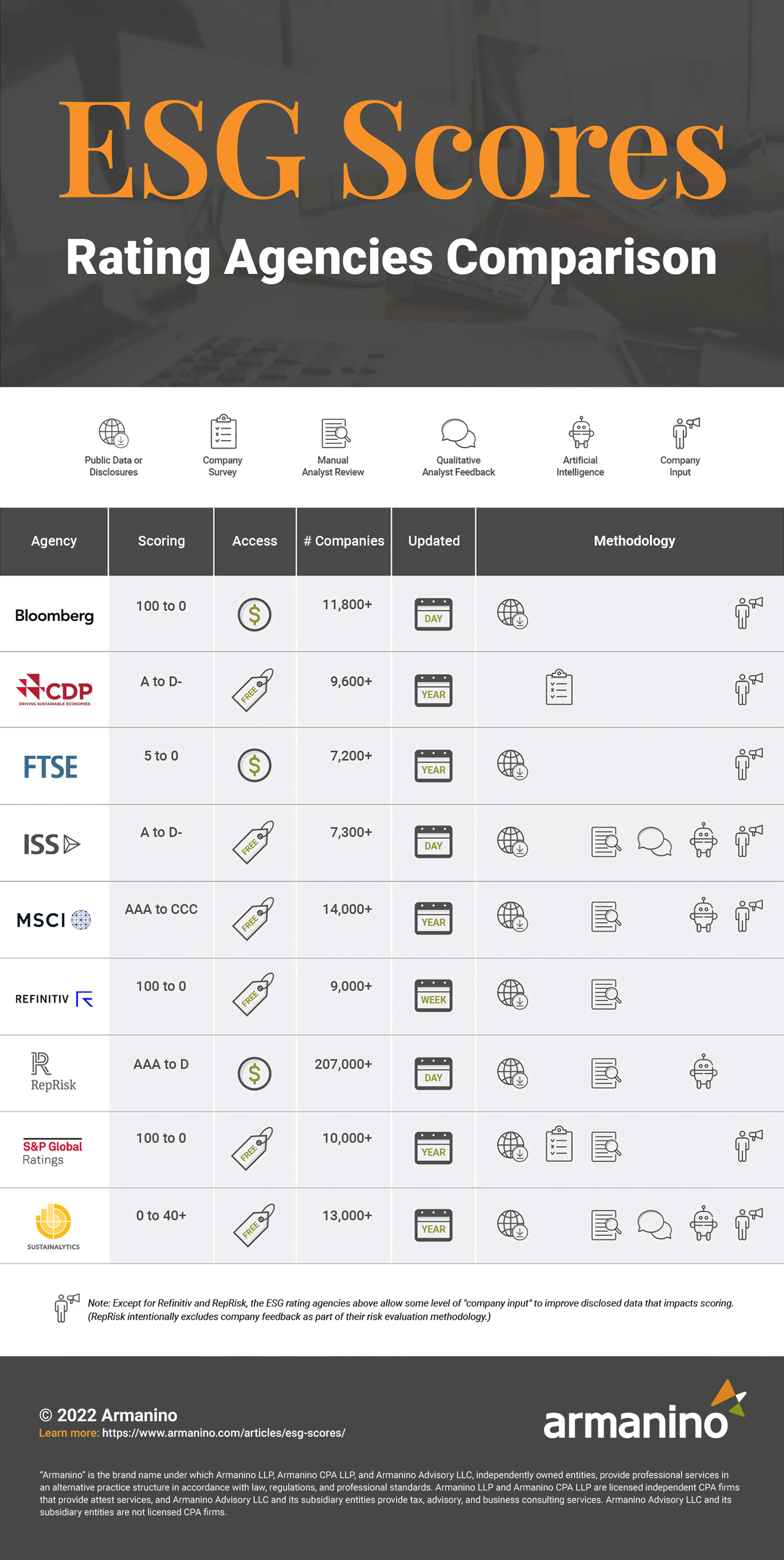
Many ESG rating agencies exist around the world today. The following are some of the most commonly used for ESG scoring.
Want to display this infographic on your site? Copy and paste the following code. Be sure to include attribution to armanino.com with this graphic.
To aid detailed comparison, each agency is described below with the following attributes:
The most popular ESG rating agencies for financial purposes are listed alphabetically below with detailed summaries.
Note: A Bloomberg Terminal subscription is required to access the data. The platform also displays CDP, ISS, RobecoSAM, and Sustainalytics scores for ESG.
Bloomberg Intelligence ESG Dashboard – E&S Score Example. Source

Note: CDP is both a score and an ESG framework. A purchase is required to access granular scoring.
CDP Climate Score Example 2021 - HCL Technologies

CDP Forests Score Example 2021 - Taylor Wimpey

CDP Water Score Example 2019 - Dover Corporation

(A subsidiary of LSEG, the London Stock Exchange Group)
FTSE Russel ESG Ratings Data Model. Source

(Formerly “ISS-oekom”)
ISS ESG Rating Example - Microsoft Corporation

MSCI ESG Rating Example - Microsoft Corporation

(In 2021, acquired by LSEG, the London Stock Exchange Group. Prior to 2018, known as “Thomson Reuters Financial & Risk” or “Reuters ESG Scores”)
Refinitiv ESG Score Example – Microsoft Corp

RepRisk ESG Ratings - Source

S&P Global ESG Scores are sometimes referenced as CSA scores or DJSI ESG scores. The Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI) uses S&P Global data.
TruCost is a now part of S&P Global.
S&P Global ESG Score Sample – Microsoft Corporation

Features a two-dimensional materiality framework to measure industry-specific risks as well as five risk levels.
Learn more about Sustainalytics
Note: In July 2020, Sustainalytics became a subsidiary of Morningstar, one of the world’s largest stock market data providers.
Sustainalytics ESG Risk Report Sample - Source

Receiving a subpar ESG score isn’t the end of the road for any organization. ESG is an ongoing process. There are many ways organizations can improve their ESG scores.
Organizations should prioritize updating their ESG strategy periodically when new risks and opportunities arise. They should also conduct an ESG materiality assessment, if they have yet to do so, to highlight ESG strengths and weaknesses. Finally, organizations that need support should consider ESG consulting services.
Whether you’re preparing for ESG disclosure or want to improve your ESG score, Armanino is here to support you. Contact our ESG consultants today!
From risk assessments and framework selection to report guidance and independent assurance of data, our team can assist your ESG strategy and efforts.